Respiration – GCSE Biology
Topic Overview
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells release energy from glucose to perform life functions. It is a vital process in all living organisms and often appears in GCSE Biology exams.
Key Concept Notes
- Respiration occurs in the mitochondria of cells.
- Glucose is broken down to release energy in the form of ATP.
- There are two types of respiration: aerobic and anaerobic.
- Aerobic equation: Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
- Anaerobic (muscles) equation: Glucose → Lactic acid + Energy
- Oxygen is essential for aerobic respiration.
- Anaerobic respiration occurs when oxygen is insufficient.
Uses of Respiration
- Provides energy for growth, movement, and active transport.
- Supports enzyme reactions in cells.
- Maintains body temperature in mammals.
Diagrams

Diagram showing aerobic and anaerobic respiration
Chloroplast structure – site of photosynthesis
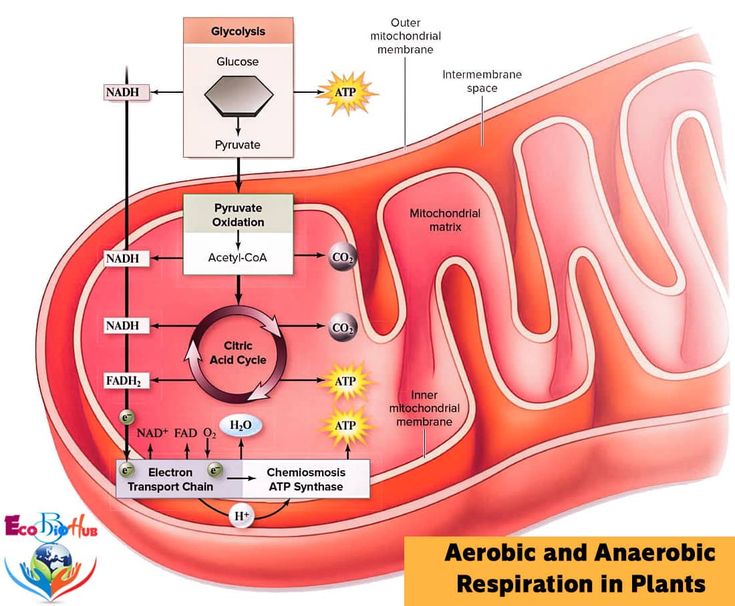
Aerobic respiration flow diagram – GCSE Biology
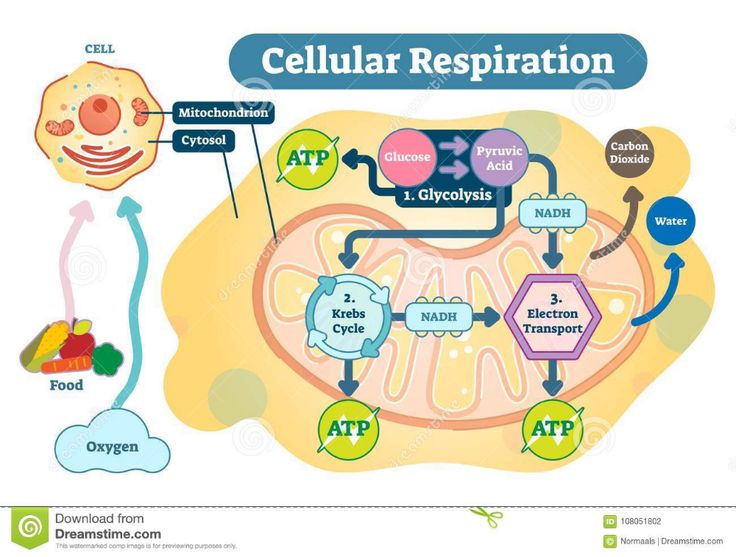
Anaerobic respiration flow diagram – GCSE Biology
6-Mark Exam Answer – Example 1
Question: Explain the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. (6 marks)
- Aerobic respiration requires oxygen, anaerobic does not.
- Aerobic respiration releases more energy (ATP) per glucose molecule.
- Aerobic equation: Glucose + Oxygen → CO₂ + Water + Energy.
- Anaerobic equation: Glucose → Lactic acid + Energy (in muscles).
- Anaerobic respiration occurs when oxygen supply is low.
- Aerobic occurs in mitochondria, anaerobic occurs in cytoplasm.
6-Mark Exam Answer – Example 2
Question: Describe how energy is released from glucose. (6 marks)
- Glucose enters the cell and is broken down in cytoplasm initially.
- In the presence of oxygen, it continues in mitochondria.
- This releases energy in the form of ATP.
- Carbon dioxide and water are produced as by-products.
- Without oxygen, anaerobic respiration occurs producing lactic acid.
- ATP produced is used for cell functions like growth and movement.
Examiner Tips
- Always mention mitochondria and ATP.
- State whether the process is aerobic or anaerobic.
- Use correct chemical equations.
- Write in 6 logical points for 6-mark questions.
- Include diagrams to support your answer where possible.
