Case Study 1: Production of Sound
Reena struck a tuning fork on a rubber pad and brought it near her ear. She noticed vibrations in its prongs, and a humming sound was produced. Sound is produced by vibrating bodies and requires a medium for propagation.
Questions:
- Sound is produced due to:
(a) heat (b) vibration (c) pressure (d) none
Answer: (b) - Medium required for sound:
(a) solid (b) liquid (c) gas (d) all of these
Answer: (d) - Can sound travel in vacuum?
(a) Yes (b) No (c) Sometimes (d) None
Answer: (b) - Unit of frequency = ?
(a) m/s (b) hertz (c) newton (d) pascal
Answer: (b) - High frequency sound is called:
(a) infrasound (b) audible (c) ultrasound (d) none
Answer: (c)
Case Study 2: Longitudinal Waves
A slinky experiment was performed in class. When compressed at one end, compressions and rarefactions travelled through the slinky, showing that sound travels as longitudinal waves.
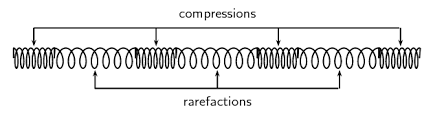
Questions:
- Sound waves in air are:
(a) transverse (b) longitudinal (c) both (d) none
Answer: (b) - Region of high pressure = ?
(a) compression (b) rarefaction (c) equilibrium (d) none
Answer: (a) - Region of low pressure = ?
(a) compression (b) rarefaction (c) crest (d) trough
Answer: (b) - Distance between two consecutive compressions = ?
(a) amplitude (b) wavelength (c) frequency (d) none
Answer: (b) - Time taken for 1 vibration = ?
(a) frequency (b) wavelength (c) time period (d) none
Answer: (c)
Case Study 3: Speed of Sound
During a thunderstorm, Neha saw lightning first and heard thunder after a few seconds. Sound travelled slower than light.
Questions:
- Speed of sound in air at 25°C ≈ ?
(a) 150 m/s (b) 300 m/s (c) 340 m/s (d) 3 × 10⁸ m/s
Answer: (c) - Speed of light in air = ?
(a) 3 × 10⁸ m/s (b) 3 × 10⁵ m/s (c) 300 m/s (d) 150 m/s
Answer: (a) - Which reaches first:
(a) light (b) sound (c) both together (d) none
Answer: (a) - Speed of sound depends on:
(a) medium (b) temperature (c) elasticity & density of medium (d) all
Answer: (d) - Sound travels fastest in:
(a) solids (b) liquids (c) gases (d) vacuum
Answer: (a)
Case Study 4: Echo
Ravi shouted in a valley and heard his own voice after 2 seconds. Echo is the reflection of sound.

Questions:
- Echo is due to:
(a) refraction (b) reflection (c) diffraction (d) interference
Answer: (b) - Speed of sound in air = 340 m/s. Distance of cliff if echo heard after 2 s = ?
(a) 170 m (b) 340 m (c) 510 m (d) 680 m
Answer: (b) - Minimum distance for echo = ?
(a) 17 m (b) 34 m (c) 68 m (d) 10 m
Answer: (b) - Time gap required between sound and echo = ?
(a) 0.01 s (b) 0.1 s (c) 0.2 s (d) > 0.1 s
Answer: (d) - Echoes are used in:
(a) SONAR (b) radars (c) medical ultrasound (d) all
Answer: (d)
Case Study 5: SONAR
Ships use SONAR to detect the depth of the ocean by sending ultrasound waves and detecting the reflected signal.
Questions:
- Full form of SONAR:
(a) Sound Navigation and Ranging (b) Sound Normal and Radiation (c) Sound Neutral and Range (d) none
Answer: (a) - Waves used in SONAR:
(a) audible (b) infrasound (c) ultrasound (d) none
Answer: (c) - Depth = ?
(a) speed × time/2 (b) speed × time (c) time/speed (d) none
Answer: (a) - If ultrasound takes 2 s to return, speed = 1500 m/s, depth = ?
(a) 750 m (b) 1500 m (c) 3000 m (d) none
Answer: (a) - SONAR used for:
(a) ocean depth (b) submarines (c) fishing (d) all
Answer: (d)
Case Study 6: Characteristics of Sound – Loudness
Two friends spoke: one softly, one loudly. Both had same pitch but different amplitudes. Loudness depends on amplitude of vibration.
Questions:
- Loudness depends on:
(a) frequency (b) amplitude (c) wavelength (d) time
Answer: (b) - Unit of loudness = ?
(a) hertz (b) decibel (c) newton (d) joule
Answer: (b) - Higher amplitude = ?
(a) louder sound (b) softer sound (c) no sound (d) none
Answer: (a) - Amplitude doubled, loudness increases:
(a) 2 times (b) 4 times (c) 8 times (d) none
Answer: (b) - Which damages ears?
(a) < 60 dB (b) > 120 dB (c) 20 dB (d) none
Answer: (b)
Case Study 7: Pitch
A boy played a flute and a drum. Flute produced high-pitched sound, drum produced low-pitched sound. Pitch depends on frequency.
Questions:
- Pitch depends on:
(a) amplitude (b) frequency (c) wavelength (d) speed
Answer: (b) - Higher frequency = ?
(a) lower pitch (b) higher pitch (c) no pitch (d) none
Answer: (b) - Male voices usually have:
(a) higher pitch (b) lower pitch (c) same (d) none
Answer: (b) - Unit of frequency = ?
(a) decibel (b) hertz (c) joule (d) watt
Answer: (b) - Pitch helps us distinguish:
(a) loudness (b) shrillness of sound (c) speed (d) direction
Answer: (b)
Case Study 8: Quality (Timbre)
Two instruments (violin and harmonium) play the same note at same loudness and pitch but still sound different. This difference is due to quality/timbre.
Questions:
- Quality of sound distinguishes:
(a) loudness (b) pitch (c) source of sound (d) none
Answer: (c) - Same pitch & loudness but different sound = due to:
(a) frequency (b) harmonics (c) velocity (d) none
Answer: (b) - Human ear can hear range = ?
(a) 2 – 20 Hz (b) 20 – 20,000 Hz (c) 200 – 200,000 Hz (d) none
Answer: (b) - Infrasonic sounds < ?
(a) 2 Hz (b) 20 Hz (c) 200 Hz (d) none
Answer: (b) - Ultrasonic sounds > ?
(a) 2000 Hz (b) 20,000 Hz (c) 200,000 Hz (d) none
Answer: (b)
Case Study 9: Hearing Range in Animals
Dogs can hear sounds of higher frequency than humans, while elephants communicate with infrasound.
Questions:
- Human hearing range = ?
(a) 2–20 Hz (b) 20–20,000 Hz (c) 200–200,000 Hz (d) none
Answer: (b) - Dog can hear:
(a) infra (b) ultra (c) both (d) none
Answer: (b) - Elephants use:
(a) infrasonic sound (b) ultrasonic (c) both (d) none
Answer: (a) - Bats navigate by:
(a) infrasound (b) ultrasound (c) audible sound (d) none
Answer: (b) - Whales communicate by:
(a) ultrasound (b) infrasound (c) audible (d) none
Answer: (b)
Case Study 10: Noise Pollution
Arjun lives near a busy road and often hears honking, causing headaches and irritation. Noise is unwanted sound, and exposure above 120 dB is harmful.
Questions:
- Noise pollution is caused by:
(a) vehicles (b) loudspeakers (c) machines (d) all
Answer: (d) - Harmful effects of noise:
(a) loss of hearing (b) lack of sleep (c) stress (d) all
Answer: (d) - Safe noise level = ?
(a) < 60 dB (b) < 80 dB (c) < 100 dB (d) none
Answer: (a) - Solution = ?
(a) planting trees (b) using silenced devices (c) reducing horns (d) all
Answer: (d) - Prolonged exposure > 120 dB leads to:
(a) hearing damage (b) sharp vision (c) high energy (d) none
Answer: (a)
