Case Study 1: Playground Circle
A circular playground has a chord AB of length 12 m. The perpendicular from the center O to AB meets it at point M, where OM = 4 m.
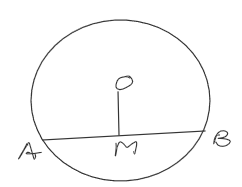
Questions:
- In a circle, perpendicular from center to chord:
(a) bisects the chord (b) doubles the chord (c) tangent to chord (d) none
Answer: (a) - If AB = 12, then AM = ?
(a) 4 (b) 5 (c) 6 (d) 12
Answer: (c) - Using Pythagoras, OA² = AM² + OM². OA = ?
(a) 5√2 (b) √52 (c) √52 = 2√13 (d) none
Answer: (c) - OA is:
(a) radius (b) diameter (c) chord (d) tangent
Answer: (a) - Length of radius = ?
(a) 6 (b) 4 (c) 2√13 (d) 12
Answer: (c)
Case Study 2: Circular Fountain
In a park, there is a circular fountain with diameter 14 m. A student walked halfway around it, subtending an angle at the center.
Questions:
- Diameter = ?
(a) 7 (b) 14 (c) 28 (d) none
Answer: (b) - Radius = ?
(a) 7 (b) 14 (c) 21 (d) none
Answer: (a) - Semicircle subtends an angle at the center = ?
(a) 90° (b) 120° (c) 180° (d) 60°
Answer: (c) - At the circumference, semicircle subtends angle = ?
(a) 180° (b) 120° (c) 90° (d) 60°
Answer: (c) - Angle in semicircle is:
(a) right angle (b) acute angle (c) obtuse angle (d) none
Answer: (a)
Case Study 3: Clock Design
A clock is circular. At 3 o’clock, hands of the clock subtend 90° at the center.
Questions:
- Angle subtended by arc of 3 hours at center = ?
(a) 30° (b) 60° (c) 90° (d) 180°
Answer: (c) - Each hour subtends at center = ?
(a) 15° (b) 30° (c) 45° (d) 60°
Answer: (b) - If arc subtends 90° at center, then at circumference it subtends = ?
(a) 90° (b) 45° (c) 60° (d) 30°
Answer: (b) - This shows:
(a) angle at center = 2 × angle at circumference (b) equal angles (c) tangent theorem (d) none
Answer: (a) - Shape of clock is:
(a) polygon (b) circle (c) quadrilateral (d) none
Answer: (b)
Case Study 4: Cyclic Quadrilateral
A quadrilateral ABCD is inscribed in a circle. ∠A = 100°, ∠C = ?
Questions:
- Opposite angles of cyclic quadrilateral are:
(a) supplementary (b) equal (c) complementary (d) none
Answer: (a) - If ∠A = 100°, ∠C = ?
(a) 80° (b) 100° (c) 90° (d) 120°
Answer: (a) - If ∠B = 85°, then ∠D = ?
(a) 95° (b) 105° (c) 85° (d) 75°
Answer: (b) - Property used = ?
(a) angle sum property (b) cyclic quadrilateral theorem (c) Pythagoras (d) none
Answer: (b) - Sum of opposite ∠ = ?
(a) 100° (b) 180° (c) 90° (d) none
Answer: (b)
Case Study 5: Wheel Rim (Equal Chords)
In a wheel rim, two equal chords AB and CD are drawn.
Questions:
- Equal chords in a circle are equidistant from:
(a) diameter (b) tangent (c) center (d) none
Answer: (c) - If AB = CD, then distance OA = distance OC.
True / False?
Answer: True - If OA = 5 and OC = 5, then radius is same for both.
Answer: True - Which theorem is used?
(a) Equal chords → equal distances from center (b) Converse of above (c) both (d) none
Answer: (c) - Wheel rim is:
(a) circle (b) polygon (c) quadrilateral (d) none
Answer: (a)
Case Study 6: Park Pathway (Arc Angles)
In a circular park, arc PQ subtends ∠POQ = 100° at center.
Questions:
- At circumference, angle subtended = ?
(a) 100° (b) 50° (c) 200° (d) none
Answer: (b) - Relation between center angle and circumference angle = ?
(a) equal (b) double (c) half (d) none
Answer: (b) - If another point R on circumference also subtends arc PQ, ∠PRQ = ?
(a) 50° (b) 100° (c) 200° (d) none
Answer: (a) - This property is known as:
(a) angle in same segment theorem (b) Pythagoras (c) tangent theorem (d) none
Answer: (a) - Circle’s radius remains:
(a) fixed (b) changing (c) variable (d) none
Answer: (a)
Case Study 7: Tangent to Circle
A tangent touches circle at point A. Center O joins OA.
Questions:
- OA ⟂ tangent at A. True/False?
Answer: True - Angle between radius and tangent = ?
(a) 30° (b) 45° (c) 60° (d) 90°
Answer: (d) - Tangent to circle touches it at:
(a) one point (b) two points (c) infinite points (d) none
Answer: (a) - Number of tangents through a point on circle = ?
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) infinite
Answer: (b) - If radius = 7, tangent length from point of contact to center = ?
(a) 7 (b) 14 (c) 49 (d) none
Answer: (a)
Case Study 8: Circular Pond
A circular pond has a bridge AB across it through the center.
Questions:
- AB passing through center is:
(a) chord (b) radius (c) diameter (d) tangent
Answer: (c) - Diameter = 2 × radius. True/False?
Answer: True - If AB = 14, radius = ?
(a) 7 (b) 14 (c) 28 (d) none
Answer: (a) - Diameter always passes through:
(a) circumference only (b) center (c) tangent (d) none
Answer: (b) - Largest chord of circle = ?
(a) radius (b) tangent (c) diameter (d) none
Answer: (c)
Case Study 9: Playground Track
Four students ran around a circular track, starting at A and meeting again after one full round.
Questions:
- Their path is along the:
(a) circumference (b) diameter (c) radius (d) tangent
Answer: (a) - Circumference = ?
(a) 2πr (b) πr² (c) 2r (d) none
Answer: (a) - If r = 7, circumference = ?
(a) 22 (b) 44 (c) 44 cm (d) 44 m
Answer: (d) - Track shape = ?
(a) polygon (b) circle (c) ellipse (d) rectangle
Answer: (b) - Formula for area of circle = ?
(a) πr² (b) 2πr (c) 2r (d) none
Answer: (a)
Case Study 10: Street Light Pole
A circular lamp is fixed with wires forming cyclic quadrilateral around it.
Questions:
- Quadrilateral inscribed in circle is:
(a) trapezium (b) cyclic quadrilateral (c) parallelogram (d) none
Answer: (b) - Opposite angles of cyclic quadrilateral are:
(a) supplementary (b) equal (c) complementary (d) none
Answer: (a) - If ∠A = 110°, ∠C = ?
(a) 70° (b) 80° (c) 90° (d) none
Answer: (a) - If ∠B = 95°, ∠D = ?
(a) 85° (b) 90° (c) 95° (d) none
Answer: (a) - Sum of opposite angles = ?
(a) 100° (b) 180° (c) 270° (d) none
Answer: (b)
