Case Study 1: Salt Solution
Riya dissolved 20 g of salt in 100 mL of water and stirred well. The salt completely disappeared, forming a clear liquid.

Questions:
- The mixture formed is:
(a) heterogeneous (b) homogeneous (c) suspension (d) colloid
Answer: (b) - Salt in the solution is the:
(a) solvent (b) solute (c) mixture (d) none
Answer: (b) - Water in the solution is the:
(a) solvent (b) solute (c) mixture (d) none
Answer: (a) - The solution formed is:
(a) opaque (b) transparent (c) translucent (d) coloured
Answer: (b) - This is an example of:
(a) compound (b) solution (c) suspension (d) colloid
Answer: (b)
Case Study 2: Chalk in Water
Sahil mixed chalk powder with water. The mixture looked cloudy and the particles settled down after some time.

Questions:
- This mixture is:
(a) solution (b) suspension (c) colloid (d) compound
Answer: (b) - A suspension is:
(a) transparent (b) translucent (c) opaque (d) clear
Answer: (c) - Tyndall effect is shown by:
(a) solution (b) suspension (c) both (b) and (c) (d) none
Answer: (c) - Size of particles in suspension is:
(a) < 1 nm (b) 1–1000 nm (c) > 1000 nm (d) none
Answer: (c) - Suspension is:
(a) stable (b) unstable (c) chemically bonded (d) none
Answer: (b)
Case Study 3: Milk
Priya poured milk into a glass. When light passed through it, the path of the light became visible.
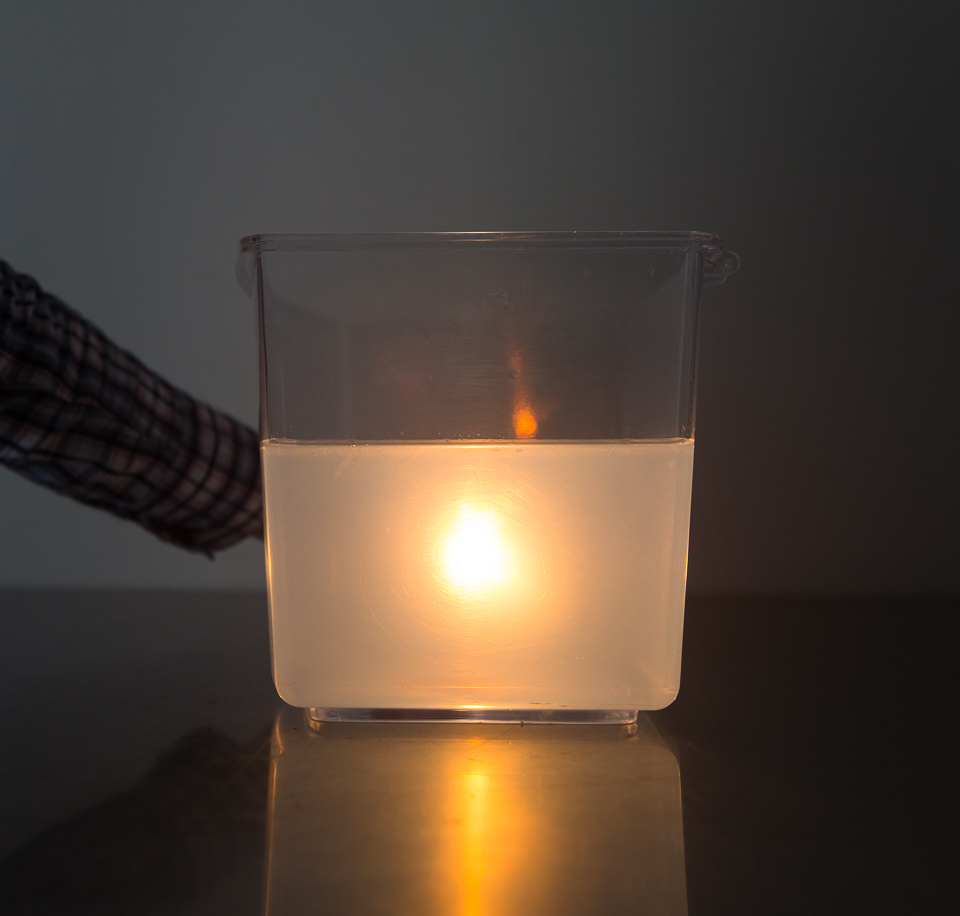

Questions:
- Milk is a:
(a) solution (b) suspension (c) colloid (d) element
Answer: (c) - Colloid shows:
(a) no Tyndall effect (b) Tyndall effect (c) always transparent (d) none
Answer: (b) - In milk, dispersed phase is:
(a) water (b) fat droplets (c) sugar (d) none
Answer: (b) - Medium in milk is:
(a) water (b) fat (c) sugar (d) none
Answer: (a) - Colloids are:
(a) heterogeneous (b) homogeneous (c) both (d) none
Answer: (a)
Case Study 4: Separating Salt from Water
A teacher heated salt water in a china dish. After some time, the water evaporated and salt remained.
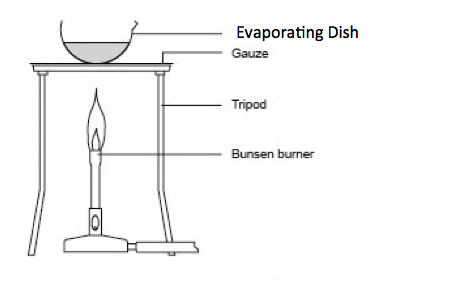
Questions:
- Technique used = ?
(a) filtration (b) evaporation (c) distillation (d) crystallization
Answer: (b) - Salt is recovered because it is:
(a) volatile (b) non-volatile (c) soluble (d) none
Answer: (b) - This is a method of separating:
(a) volatile solute from solvent (b) volatile solvent from solute (c) solid from liquid (d) none
Answer: (c) - This method is best for:
(a) sugar + water (b) salt + water (c) alcohol + water (d) none
Answer: (b) - Process involved:
(a) physical change (b) chemical change (c) both (d) none
Answer: (a)
Case Study 5: Ink Separation
Teacher placed a drop of blue ink on filter paper and dipped it in water. Different colours rose at different heights.
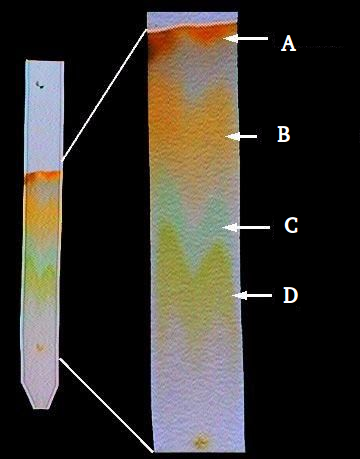
Questions:
- Technique used = ?
(a) filtration (b) evaporation (c) chromatography (d) centrifugation
Answer: (c) - Chromatography is used to separate:
(a) insoluble solids (b) coloured solutes (c) gases (d) none
Answer: (b) - Solvent moves up the paper due to:
(a) capillary action (b) gravity (c) evaporation (d) none
Answer: (a) - This method works on principle of:
(a) different solubility (b) density difference (c) volatility (d) none
Answer: (a) - This experiment shows ink is:
(a) pure (b) mixture of dyes (c) element (d) compound
Answer: (b)
Case Study 6: Petroleum Refining
Petroleum is separated into petrol, diesel, kerosene etc. using fractional distillation.
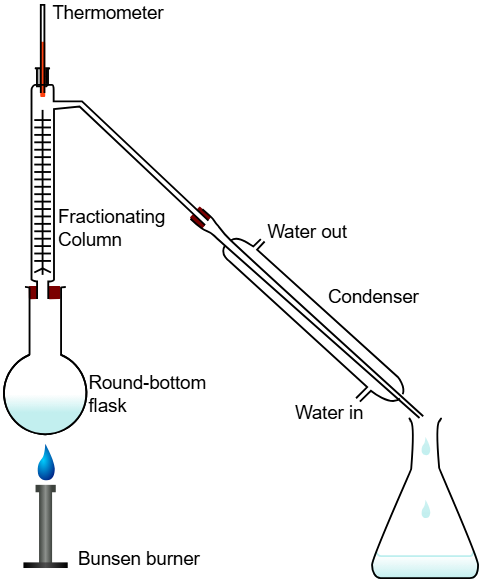
Questions:
- Technique used = ?
(a) distillation (b) fractional distillation (c) chromatography (d) filtration
Answer: (b) - Principle:
(a) different boiling points (b) solubility (c) density (d) none
Answer: (a) - Petroleum is a:
(a) compound (b) element (c) mixture (d) colloid
Answer: (c) - Petrol boils at a:
(a) higher temp than diesel (b) lower temp than diesel (c) equal temp (d) none
Answer: (b) - Fractional distillation separates:
(a) solids (b) miscible liquids (c) gases (d) none
Answer: (b)
Case Study 7: Iron and Sulphur
When iron filings are mixed with sulphur powder, a yellow-black mixture is formed. On heating strongly, a black solid (FeS) is formed.
Questions:
- Iron + Sulphur (without heating) is:
(a) compound (b) mixture (c) element (d) none
Answer: (b) - After heating → FeS is:
(a) mixture (b) compound (c) element (d) none
Answer: (b) - Property of FeS different from iron and sulphur proves:
(a) mixture formed (b) compound formed (c) colloid formed (d) none
Answer: (b) - Magnet can separate iron from:
(a) FeS (b) Fe + S mixture (c) both (d) none
Answer: (b) - Heating mixture shows:
(a) physical change (b) chemical change (c) both (d) none
Answer: (b)
Case Study 8: Blood Separation
In a laboratory, blood is rotated in a centrifuge to separate plasma and cells.
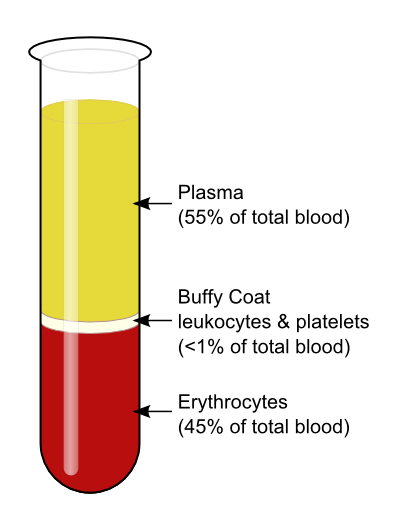
Questions:
- Technique used = ?
(a) filtration (b) evaporation (c) centrifugation (d) sublimation
Answer: (c) - Separation is based on:
(a) solubility (b) density difference (c) volatility (d) boiling point
Answer: (b) - Plasma appears as:
(a) red layer (b) yellowish layer (c) white layer (d) none
Answer: (b) - RBCs settle at:
(a) bottom (b) top (c) middle (d) none
Answer: (a) - This is used in:
(a) dairies (b) medical labs (c) both (d) none
Answer: (c)
Case Study 9: Distilled Water vs Tap Water
Rahul tasted distilled water and tap water. Distilled water had no taste, while tap water tasted slightly salty.
Questions:
- Distilled water is:
(a) pure compound (b) mixture (c) element (d) colloid
Answer: (a) - Tap water is:
(a) pure (b) mixture (solution) (c) element (d) colloid
Answer: (b) - Salts in tap water make it:
(a) taste sweet (b) taste salty (c) tasteless (d) none
Answer: (b) - Distilled water is obtained by:
(a) evaporation (b) distillation (c) sublimation (d) filtration
Answer: (b) - Tap water is:
(a) homogeneous mixture (b) heterogeneous mixture (c) colloid (d) compound
Answer: (a)
Case Study 10: Air as a Mixture
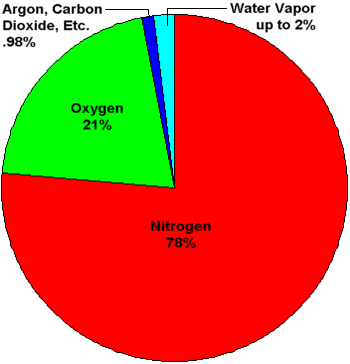
Air contains nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapour and some dust particles.
Questions:
- Air is a:
(a) compound (b) mixture (c) element (d) colloid
Answer: (b) - Major component of air = ?
(a) oxygen (b) nitrogen (c) CO₂ (d) water vapour
Answer: (b) - Oxygen percentage in air ≈ ?
(a) 21% (b) 78% (c) 1% (d) 0.03%
Answer: (a) - Air is separated into gases by:
(a) fractional distillation of liquid air (b) chromatography (c) centrifugation (d) none
Answer: (a) - Air supports life due to:
(a) nitrogen (b) oxygen (c) carbon dioxide (d) dust
Answer: (b)
